Recently, a paper entitled “Generalized and Discriminative Collaborative Representation for Multiclass Classification” has been published online in IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics. The paper is finished by a research team on machine learning with the leadership of Prof. Wang Yulong from College of Informatics and Prof. Chen Hong from College of Sciences of Huazhong Agricultural University (HZAU). Based on the low-dimensional structure information of the nature of high-dimensional data, researchers have proposed a high-dimensional data pattern classification method featuring high interpretability, strong discrimination and high efficiency.
High-dimensional data widely exist in various fields of scientific research and social life, such as high-dimensional biological gene expression data, high-dimensional medical image data, and high-resolution image (video) data in the Internet. Nevertheless, high-dimensional data often causes “dimension disaster”, reducing algorithm performance and bringing huge storage and computation burden. With profound theoretical and application values, it is how to use the internal structure information of high-dimensional data to overcome the above difficulties and then establish efficient high-dimensional data learning methods and theories that has been a hot spot in machine learning.
Given the utilization of multi-low dimensional spatial structure which acts as the core of high dimensional data, the research has designed a generalized collaborative representation-based general framework for the high dimensional data schema classification, analyzed common grounds and disparities of different representation-based classification methods from a higher perspective and presented corresponding theoretical analysis to elucidate classification principle and internal mechanism. A discriminative representation-based classification has been initiated in terms of this framework as a way to enhance the recognition of representation-based coefficient and classification performance of the algorithm. This method boasts large interpretability, strong discriminability and high efficiency and other benefits. The process of classification and recognition is as follows:
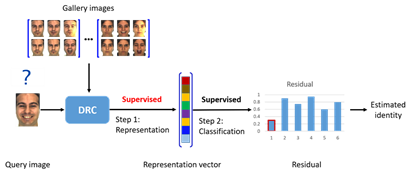
In addition, the researchers reveal the relationship between the spatial distribution of high-dimensional data and the classification performance of the DRC algorithm, and establish the corresponding theoretical guarantees. The finding will contribute to a deeper understanding of the relationship between the intrinsic structure of high-dimensional data and pattern recognition, and provide guidance for the study of high-dimensional data learning and other machine learning tasks.
Apart from previous achievements on atomic representation of high-dimensional data learning published in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence in 2019 and IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics in 2020, the research represents new progress made by the team in artificial intelligence for high-dimensional data. Prof. Wang is the first author and Prof. Chen is the corresponding author. The research has been funded by the General Project and Youth Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Link of the paper: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9210834v
Source: http://news.hzau.edu.cn/2020/1118/58789.shtml
Translated by: Sun Fei, Wang Xu, Xiong Ying, Yan Xiruo, Xiong Yong, Yu Qiuxu, Zhang Huijuan, Zhang Quan, Zhang Qian
Supervised by: Zhang Juan
